Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Ozone in the Food Industry
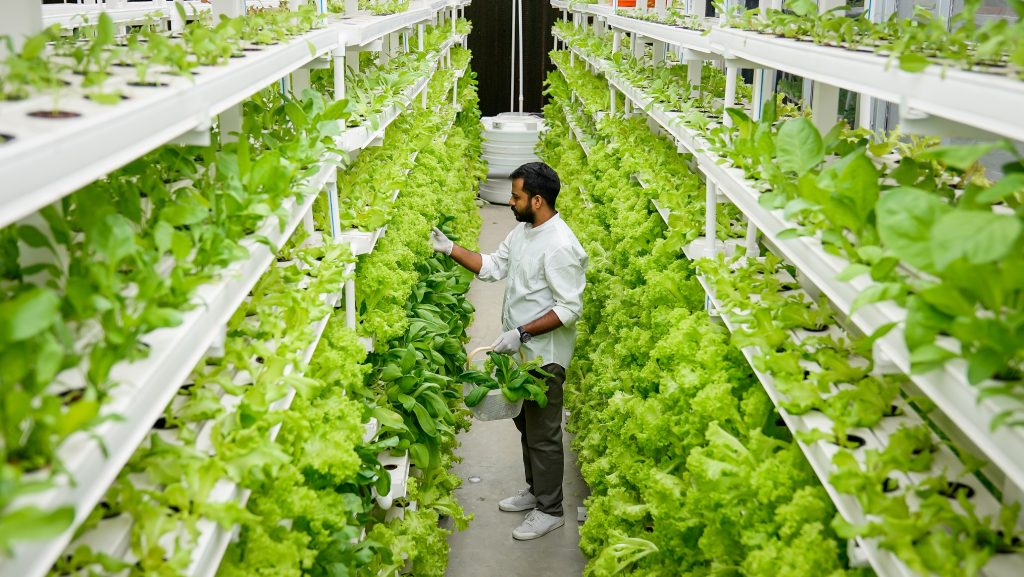
The food and beverage industry can benefit significantly from Ozone oxidants and superior antimicrobial properties, which provide advantages over traditional food preservation techniques. Ozone can kill bacteria, mold, yeasts, protozoan cysts, and viruses within a short period at low concentrations. Besides inactivating contaminant microflora on food, Ozone also reduces pesticide levels. Its rapid decomposition to oxygen and lack of toxic residues also make Ozone an environmentally friendly sanitizer.
Advantages of Ozone for food processing
Ozone is increasingly used in the food and beverage industry since the FDA granted ozone “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) status. Because Ozone breaks into oxygen without leaving harmful by-products, it is an attractive alternative to other disinfectants, including chlorine.
Ozone can be applied to fresh produce to control pathogens and extend shelf-life. For example, storage with 0.3 ppm ozone increased the shelf life of citrus fruits by one week (Palou et al. 2001). Also, Ozone extends the shelf life of blackberries by up to 12 days without affecting their anthocyanin content. (Barth et al. 1995) these are just two of the many studies available in the literature.
Each step in the food production chain has multiple potential sources of contamination. In the Pre-harvest, dirty irrigation water, manure fertilizer, and poor working conditions are the most frequent causes of contamination of fruits and vegetables. Microbial hazards in fresh fruits and vegetables can result from improper handling, storage, contaminated water, contaminated processing equipment, transportation environments, and cross-contamination from other products. Also, the loss of surface integrity during the cutting, shredding, and slicing fresh fruits and vegetables can lead to penetration and rapid growth of microorganisms.
This contamination generates significant economic losses and shortens the useful life. In addition, contamination with pathogens such as Escherichia coli or Listeria can result in serious health problems. As a result, fruits need disinfection. Ozone for food Industry disinfection is a great alternative. Washing vegetables and fruits with ozonated water can help ensure their safety. Ozone can destroy mold and bacteria and is particularly effective against E. coli, the food pathogen of most concern to the produce industry.
Applications of Ozone
Click the applications to learn more about
- Ozone Dairy
- Ozone for Cold Rooms
- Ozone for Food Safety and Sanitation
- Ozone for Fruit & Vegetable Disinfection
- Ozone for Meat, Poultry & Fish Disinfection
- Ozone for Wine & Beer
- Ozone Grain & Feed Disinfection
Ozone uses
Fruits and vegetables are highly susceptible to spoilage microorganisms. The fruit and vegetable industry can use the ozone system to destroy pathogenic microbes, spoilage microbes, and mycotoxins.
Pesticide resistance and increased demand for organic grains have caused food manufacturers and grain operators to find new ways to control insects, pathogens, and pests in stored commodities. Ozone technology can break pesticide and chemical residues. Food items with Ozone as a disinfectant have a much longer shelf life.
The microorganisms adhered to the milk contact surface are hard to destroy. Ozone treatment is a safe, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative to chloride-based sanitizers; Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent active against a wide range of microorganisms and is effective for biofilm removal.
Breweries typically clean their equipment and pipelines with hot water and cleaning chemicals. These processes are energy-intensive, and breweries incur significant costs. Additionally, residues and harmful by-products of chlorides degrade the quality of the product. There is a perfect solution to all these problems in Ozone for Wine & Beer.
The food industry can use Ozone for surface disinfection, sanitation of food plant equipment, sanitation of pipelines, and many other disinfection applications.
Our customers often ask us if Ozone can be used in their food processing or sanitizing process. The answer is simple. Because Ozone is the most potent and fastest active oxidizer commercially available today, it will work in any application where other sanitizers have been used, only quicker and cheaper—making the whole process efficient and environmentally friendly.
Safe Ozone Concentrations for Effective Food Processing
Specific concentrations of Ozone that are safe to use in food processing vary depending on the particular application and the food being treated. However, here are some general guidelines for ozone concentrations commonly used in food processing:
- Ozone concentration for water disinfection: Ozone can be dissolved in water to create ozonated water, which is commonly used for washing fruits, vegetables, and food processing equipment. The recommended concentration for water disinfection typically ranges from 0.5 to 2.0 parts per million (ppm) of Ozone.
- Ozone concentration for surface disinfection: Ozone can be applied as a gas or as aqueous ozone for surface disinfection of food plant equipment, pipelines, and other surfaces. The recommended concentration for surface disinfection is generally between 1.0 and 5.0 ppm of Ozone.
- Ozone concentration for food storage: Gaseous ozone and aqueous ozone can extend the shelf life of certain food products. The concentration of Ozone used for food storage varies depending on the type of food and desired shelf life extension. For example, dissolved ozone concentrations of around 0.3 ppm have been used for citrus fruits. In comparison, concentrations of up to 1.0 ppm have been used for berries.
It’s important to note that while Ozone can benefit food processing, high Ozone concentrations can negatively affect food quality, such as taste and texture changes. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully monitor and control dissolved ozone concentrations to ensure food safety and quality.
Please keep in mind that these are general recommendations. We can assist you with your specific application in the food processing industry. Please give us a call now.
How does Ozone compare to other disinfectants in terms of cost?
- Ozone: Ozone is generated on-site using ozone generators. The cost of ozone generation equipment and maintenance can vary. Still, overall, Ozone is considered cost-effective due to its fast action and high disinfection efficacy. Ozone systems require an initial investment but can result in long-term cost savings.
- Chlorine: Chlorine-based disinfectants are widely available and relatively inexpensive. However, costs can vary depending on the concentration and form of chlorine (e.g., liquid chlorine, chlorine gas, or solid chlorine compounds). Handling and storage of chlorine products may also incur additional costs.
- UV-C Light: UV-C light systems can have higher upfront costs for installation and equipment purchases. Additionally, UV-C lamps require periodic replacement, which adds to the maintenance cost.