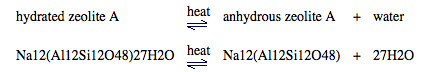Ozone Library
Uses of Zeolite For Ozone destruction
Zeolite Is Commonly Used For Ozone destruction As It Works To Accelerate The Process Of Turning Ozone Into Oxygen
– Replacing aluminum for silicon in a tetrahedron increases the net negative charge:
tetrahedron formula oxidation state oxygen oxidation state metal/semi-metal charge on a tetrahedron
SiO4 -2 +4 (Si) +4 + (4 x -2) = 4-
AlO4 -2 +3 (Al) +3 + (4 x -2) = 5-
Cations are required to balance the negative charge of the aluminosilicate framework.
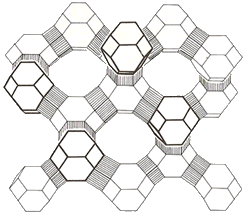
– The tetrahedra containing silicon and aluminum are arranged in three-dimensional frameworks creating interconnecting channels and resulting in structures with a large surface area.
Some of the uses of zeolites are:
- desiccation
- ion-exchange reactions
- catalysis of some reactions
- gas separation
DESICCATION
- Desiccation refers to the removal of water. Zeolites are desiccants, or drying agents, they can remove water from the atmosphere.
- Zeolite A is a synthetic zeolite commonly used in detergents as a water softener.
- Zeolite A has the formula Na12(Al12Si12O48)27H2O
- Na+ is the cations balancing the charge on the aluminosilicate ion.
- The charge on the aluminosilicate ion = 12 x +1 = 12+
- The formula of the aluminosilicate ion is Al12Si12O4812+
- The zeolite also contains 27 water of crystallization (27H2O).
- The loosely held water of crystallization can be driven out of the zeolite by heating it:
- Placing the anhydrous zeolite in moist air will result in the water being taken up by the zeolite as the system tries to re-establish equilibrium by Le Chatelier’s Principle.
CATION EXCHANGE
Within the channels in the zeolite structure, ions, such as Na+, ionically bonded to the zeolite framework, can be displaced by cations of greater charge.
Cation Exchange is determined by:
- Strength of adsorption
- Relative concentrations of cations in solution
![]()
WATER SOFTENING
Hard water containing Ca2+ or Mg2+ can be passed through a column packed with sodium zeolite, NaZ.
The dipositive Ca2+ or Mg2+ cations displace the Na+ ions from the channels within the zeolite framework:
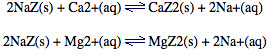
Na+ will not form a precipitate with soap like Ca2+ or Mg2+ does, so the water has been softened.
Since the cation exchange is an equilibrium reaction, it is possible to regenerate the sodium zeolite by passing a concentrated sodium chloride solution, or brine, through the zeolite.
Increasing the concentration of Na+(aq) shifts the equilibrium position to the left by Le Chatelier’s Principle, favoring the re-formation of the sodium zeolite and releasing Ca2+ or Mg2+ back into the solution.
CONTROLLED-RELEASE NITROGEN FERTILIZERS
Urea is a common, water-soluble, nitrogen fertilizer that can be leached through the root zone.
Urea is converted into ammonia by an enzyme, urease, found in many soils.
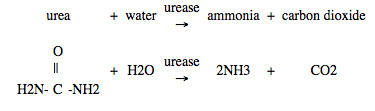
Ammonia reacts with water in the soil to form ammonium ions:
![]()
Soil bacteria convert the ammonium ions into nitrate ions which are readily leached from the soil.
Zeolites can be used to reduce the loss of this nitrogenous nutrient in three ways:
- Urea can be contained within the zeolite framework which prevents it from leaching into the root zone.
- Urea contained in the zeolite framework slows down the conversion of urea into ammonium ions by soil bacteria.
- Adsorption of ammonium ions into the zeolite’s channels protects them from nitrifying bacteria which convert them into leachable nitrate ions.
The ammonium ions are released into the soil slowly over time.
CONTROLLED-RELEASE NITROGEN FERTILIZERS
A zeolite containing an exchange ion such as ammonium can be mixed with phosphate minerals (such as apatite, calcium phosphate) to produce a controlled-release phosphorus fertilizer.
The zeolite takes up Ca2+ from the apatite and releases phosphate and ammonium ions into the soil:
![]()
As phosphate is taken up by plants, the zeolite will release more phosphate and ammonium ions in an attempt to re-establish equilibrium by Le Chatelier’s Principle.
CATALYSIS
Hydrogen ions, H+, can be incorporated into the zeolite structure in order to achieve charge compensation.
These hydrogen ions bind with bridging oxygens resulting in acidic groups.
These zeolites behave like acids and can initiate a range of chemical reactions within their channels.
Only certain shapes of molecules will be able to enter and leave the channels in the zeolite, so the zeolite catalyst is said to be shape-selective.
A particular zeolite is used in the petrochemical industry as a “cracking catalyst”.
Long-chain hydrocarbon molecules that are present in heavy oils can diffuse through the channels of the zeolite structure and into large cavities where they are attacked by the zeolite’s acidic groups and broken down (cracked) into shorter chain hydrocarbon molecules
GAS SEPARATION
Zeolites can be used to separate mixtures of different gases.
Gaseous molecules of the right shape can pass (diffuse) through the channels of the zeolite.
Gaseous molecules that are not the right shape cannot pass (diffuse) through.
Differently shaped molecules will be adsorbed into and diffused through the zeolite structure to different extents.
On-Board Oxygen Generating Systems are used in aircraft that fly at high altitudes. They use zeolites to remove nitrogen from compressed air in order to supply oxygen for aircrews.
This is because N2(g) is adsorbed more strongly than O2(g) in zeolites with low silicon to aluminum ratio.