Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Ozone FAQ
What is Ozone?
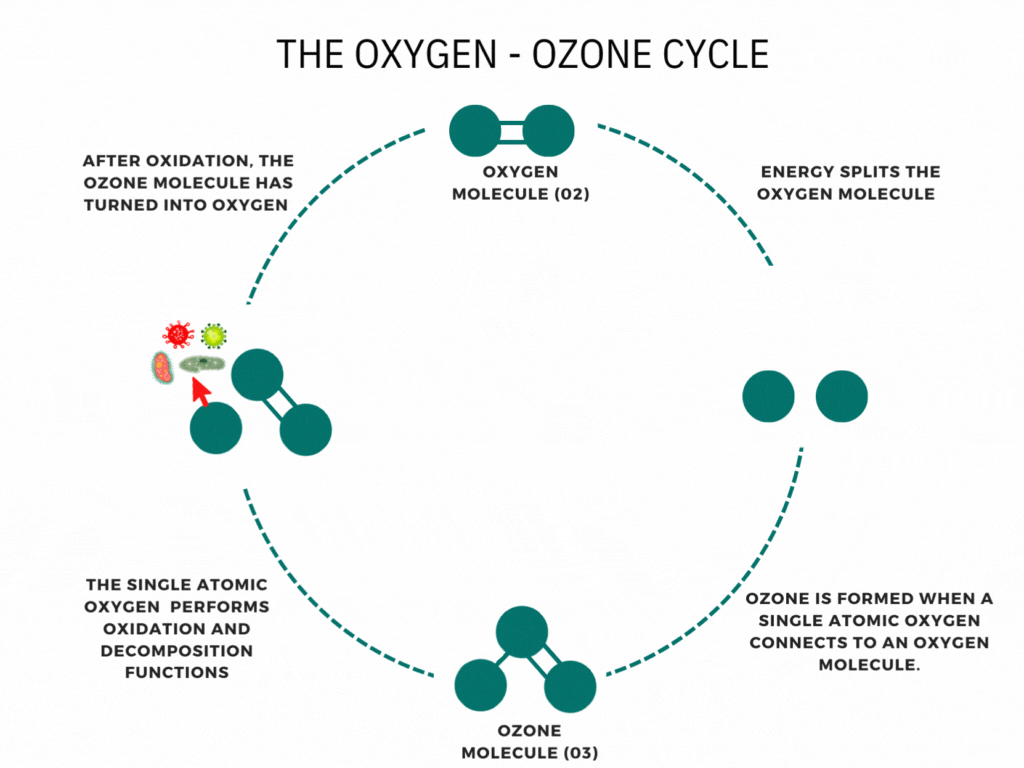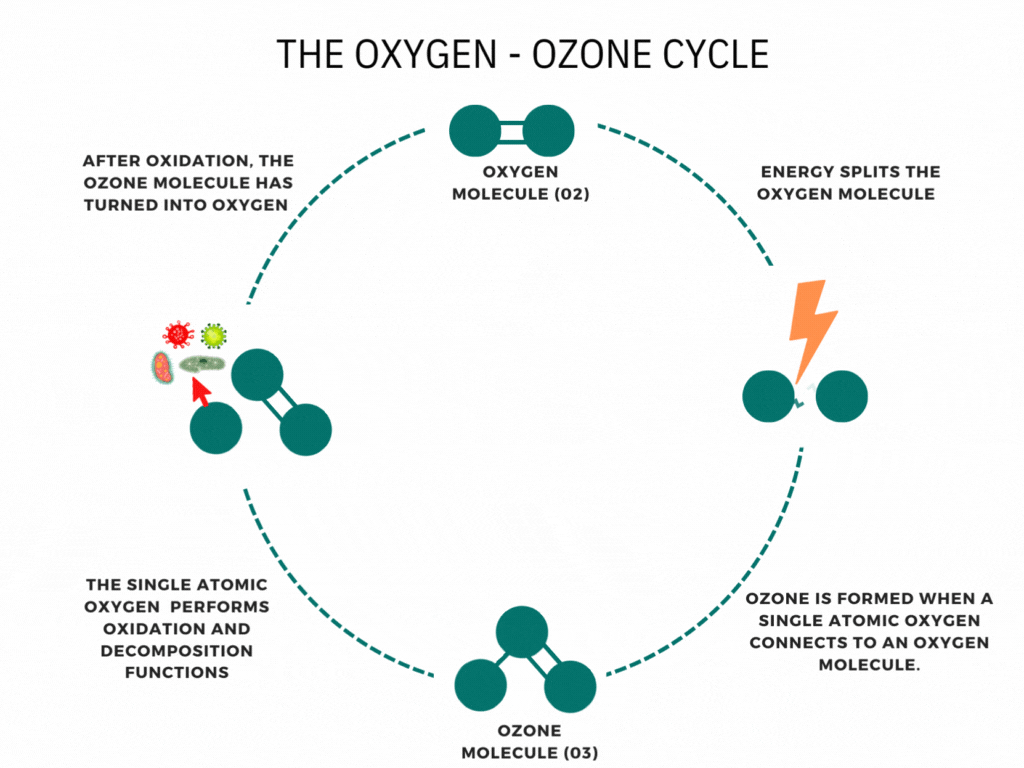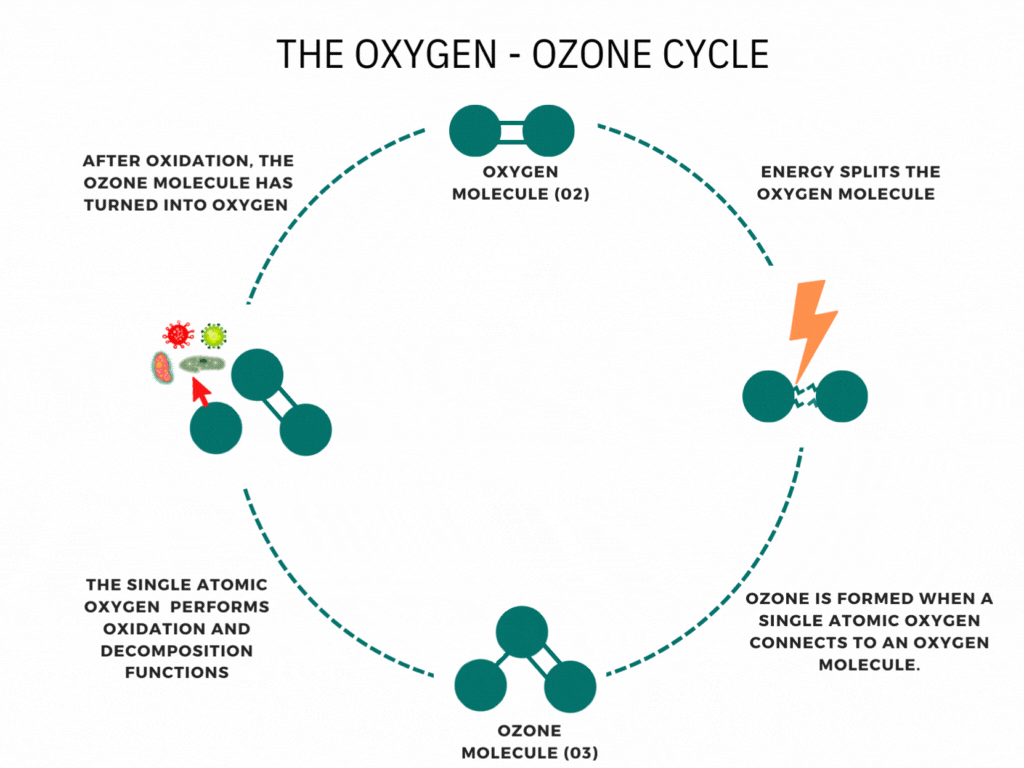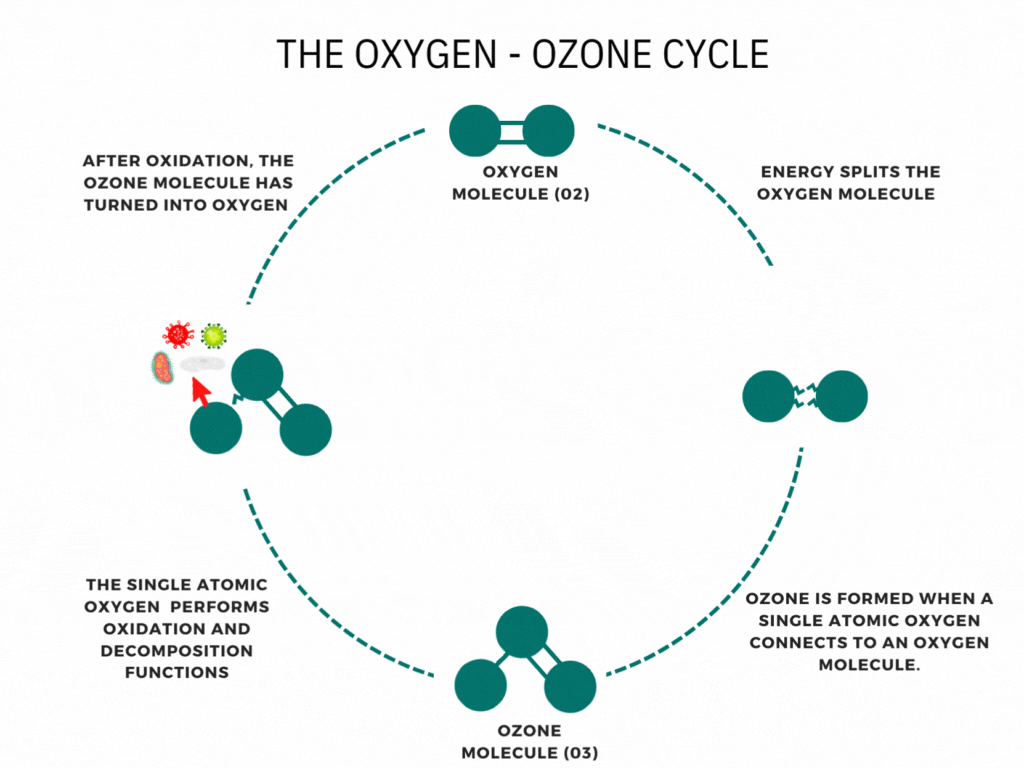
An ozone molecule is nothing more than an oxygen molecule that has received an extra oxygen atom. Nature constantly produces ozone. A well-known example is the ozone layer, created by UV rays emitted by the sun. Also, nature produces ozone during storms and waterfalls. The above examples are immediately associated with ozone when one speaks of it.
In contrast, it is less known that a generator can artificially produce ozone for disinfection purposes. Ozone generators can create ozone artificially through high voltages. The methods involve the decomposition of the oxygen molecule that causes oxygen radical formation. These oxygen radicals can bind to oxygen molecules, forming ozone (O3). The ozone molecule is volatile and has a short half-life, causing it to fall back into its original.
How does ozone work?
Ozone is known as one of the most potent oxidants. Ozone can quickly burn dissolved compounds (oxidation). The extra oxygen atom quickly binds to each component that comes in contact with ozone molecules. The instability of ozone and its inclination to return to its original form (O2) made ozone and power oxidant agent. Ozone can oxidize organic and inorganic substances, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. In the oxidation process, the extra oxygen radical from the ozone molecule reacts with other materials, leaving only pure and stable oxygen molecules (O2).
Ozone has many uses in different industries. For example, in wastewater and drinking water purification, bottled water systems, In the Food industry uses ozone for disinfection and extended shelf life. The textile industry uses ozone for colour removal and many other uses for ozone.
The most significant benefit of ozone is its pure characteristic. It only needs oxygen and energy for its formation, and as a result, byproduct formation rarely occurs and does not leave any chemical residual.
How does an ozone generator work?
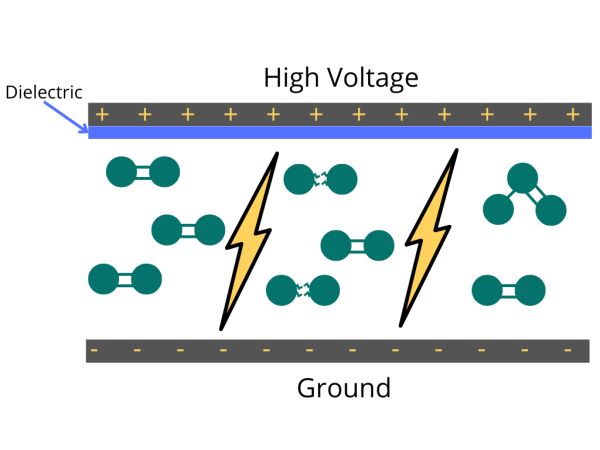
Ozone generators produce ozone (O3) by applying an electrical charge to the oxygen molecules (O2) passing through them, causing the oxygen atoms to split apart and temporarily recombine. Industrial ozone generators have cells designed to diffuse electrical discharge through a dielectric material to generate ozone.
Industrially, ozone is primarily generated with cold plasma (or dielectric barrier discharge). It is simply a diffused spark through a dielectric to spread out the electrical discharge to a large area. In this method, the electric charge applied to the electrodes causes some oxygen molecules to split apart and temporarily combine with other oxygen molecules making a molecule of three oxygen atoms (O3).
Why do I need an oxygen concentrator?
One of the first questions one often faces when designing an ozone system is whether I require concentrated oxygen or just clean, dry air. I will explain why oxygen-feed ozone generators are the best choice for all industrial applications. Industrial ozone generators use Plasma technology. Plasma Ozone generators require high oxygen concentrations and can generate ozone gas concentrations of 10-15%.
Benefits of plasma over corona discharge ozone generation
- Plasma Ozone Generators offer higher ozone gas concentrations in a smaller footprint than the equivalent Corona Discharge Ozone Generators.
- Unlike Corona Discharge Ozone Generators, Plasma Ozone Generators operate using a pure oxygen feed, so they are not affected by fluctuations in Ozone gas concentration.
- Plasma Ozone Generators do not form corrosive and toxic nitric acids as the feed gas does not contain Nitrogen and is generally moisture-free.
- Plasma Ozone Generators generate less heat than a Corona Discharge Ozone Generator of the same capacity.
What are ozone production and ozone concentration?
The performance of an ozone generator is measured by its concentration (% wt or g/m³) and production (g/hr). Both measurements are critical. But what do they mean? Ozone production refers to the mass of ozone produced over time, measured in grams per hour. It is closely related to the flow of oxygen/air at the generator inlet. Ozone concentration can be calculated by dividing total feed gas by total ozone produced (g/m³ or % by weight). For example, let’s compare two ozone generators with the same production.
Generator A: 30 g/h that required 12.5 SLPM of air. Generator B oxygen-feed 30 g/h. that only needed 4 SLPM of oxygen.
Let’s do a simple calculation to compare the concentration if you run both units for 1 hour. “Generator A” will give you 30 g of ozone, but in a mixture of 750 litres, generator B will provide you with the same 30 g but only 240 litres.
Solubility measures how much solute can be dissolved into a solvent to make a solution. An important fact is that not all ozone is soluble in water. Henry’s Law dictates (simplified) that the higher the ozone concentration, the more ozone you can dissolve in water. The ozone concentration is essential for dissolving ozone in water.
How much ozone do I need?
Dosage is the required amount of ozone. It is expressed in mg/l (milligrams per litre) or ppm (parts per million). Either value is the same. There is an extensive range of applications requiring different dosages. The following are reference values for some typical applications of ozone:
Typical Ozone Dosage:
Bottled water 0.05-0.3 ppm
Cooling towers 0.05 – 0.3 ppm
Reclaimed water 0.2 – 0.5 ppm
Bacteria & Virus 0.2 – 1.0 ppm
Contact us now if you need help with the dosage required in your applications. We have extensive experience in a wide range of applications involving ozone. We will be glad to assist you.
How long does ozone last?
It is necessary to generate ozone on-site. Because ozone has a short half-life, so it quickly decays after production. The half-life of ozone in water is about 30 minutes (depending of temperature and pressure), meaning that the ozone revert back to oxygen atom and concentration will be half that of its initial concentration every half hour.
What is ozone mass transfer?
An ozone mass transfer occurs when a gas phase moves into a liquid phase. It is usually necessary to dissolve ozone in water for most Ozone applications. There is a partial solubility of ozone gas in the liquid. However, it is possible to reach high mass transfer efficiency using proper methods and equipment. Bubbles or venturi mass transfer systems can transfer ozone. Diffusion stones were initially used to transfer ozone mass to water. Currently, venturi-based mass transfer systems are the best method for dissolving ozone in water due to their simplicity, economy, and effectiveness.
Is Ozone Harmful, and what are the long-term effects?
At higher concentrations, ozone can harm human health when inhaled. Several agencies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), have proposed maximum acceptable concentration values of 0.06 parts per million (PPM) for an 8-hour workday, five days a week.
When exposed to high ozone concentrations, people may experience dryness in the mouth and throat, coughing, headaches, and chest tightness. Taking precautions to avoid prolonged exposure to high ozone levels is essential, as these symptoms can be uncomfortable and concerning. Nevertheless, it is crucial to note that ozone can be used safely and effectively in various applications when proper precautions are taken.